- Unlocking Health Benefits with Intermittent Fasting
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: Fasting for a Healthier Diabetic Life
- Weight Loss and Better Heart Health: A Winning Combination
- Autophagy: A Cellular Cleanup Process for Better Health
- Choosing the Right Fasting Method: Find What Works for You
- Tips for Safely Incorporating IF into Your Diabetic Lifestyle
Unlocking Health Benefits with Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting (IF) is an increasingly popular dietary practice, known for its potential benefits for weight loss and overall health. For diabetics, IF offers unique advantages that can improve glucose control and reduce the risk of complications. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of intermittent fasting for diabetics, discuss different fasting methods, and provide tips for safely incorporating IF into your lifestyle.
-
Improved Blood Sugar Control: Fasting for a Healthier Diabetic Life
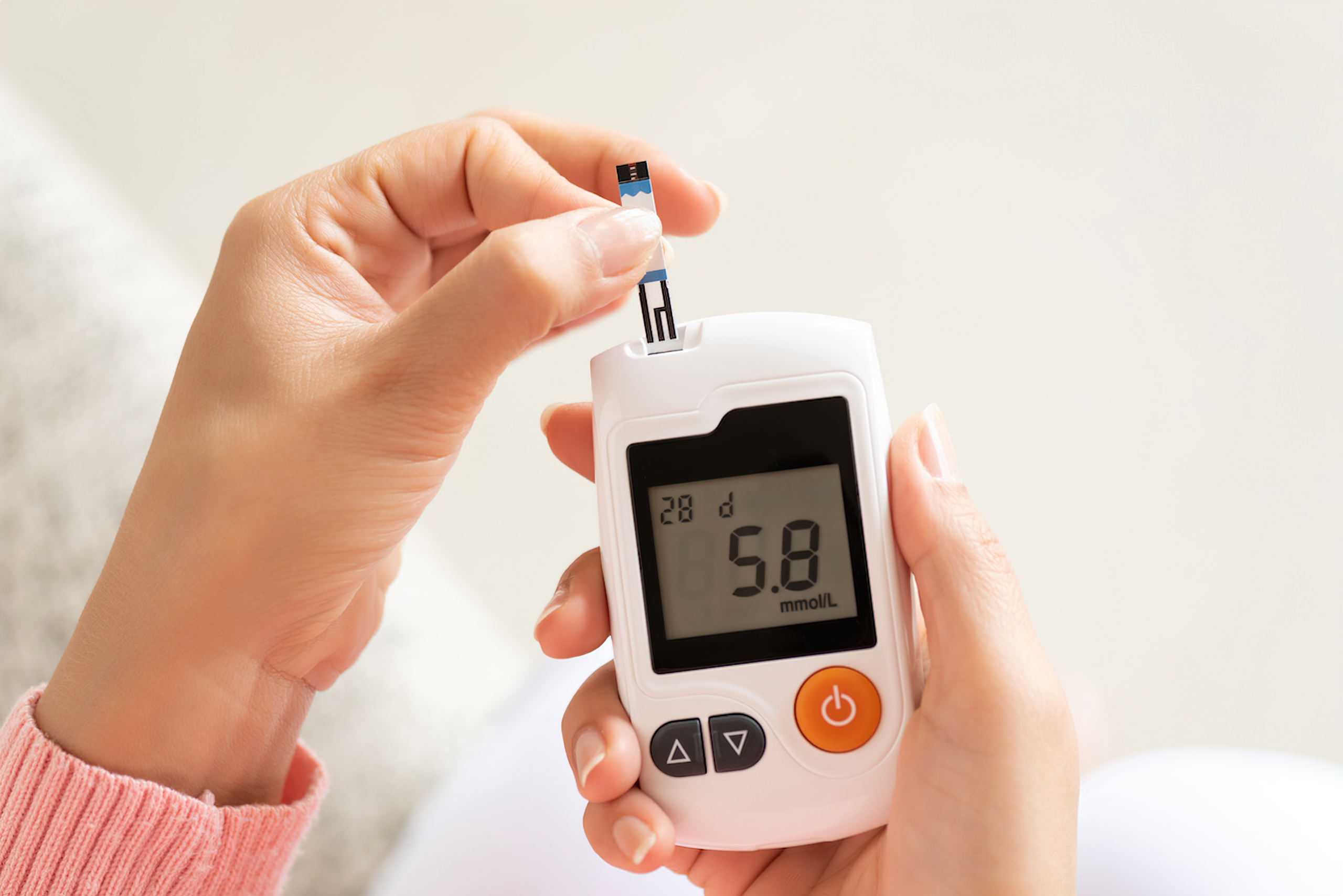
One of the main benefits of IF for diabetics is improved blood sugar control. Fasting periods can help the body become more sensitive to insulin, which is crucial for managing diabetes. During these periods, the body utilizes stored glucose and burns fat for energy, which can result in lower blood sugar levels. Short-term studies have shown that IF can reduce fasting blood glucose and HbA1c, indicating better long-term blood sugar control.
-
Weight Loss and Better Heart Health: A Winning Combination
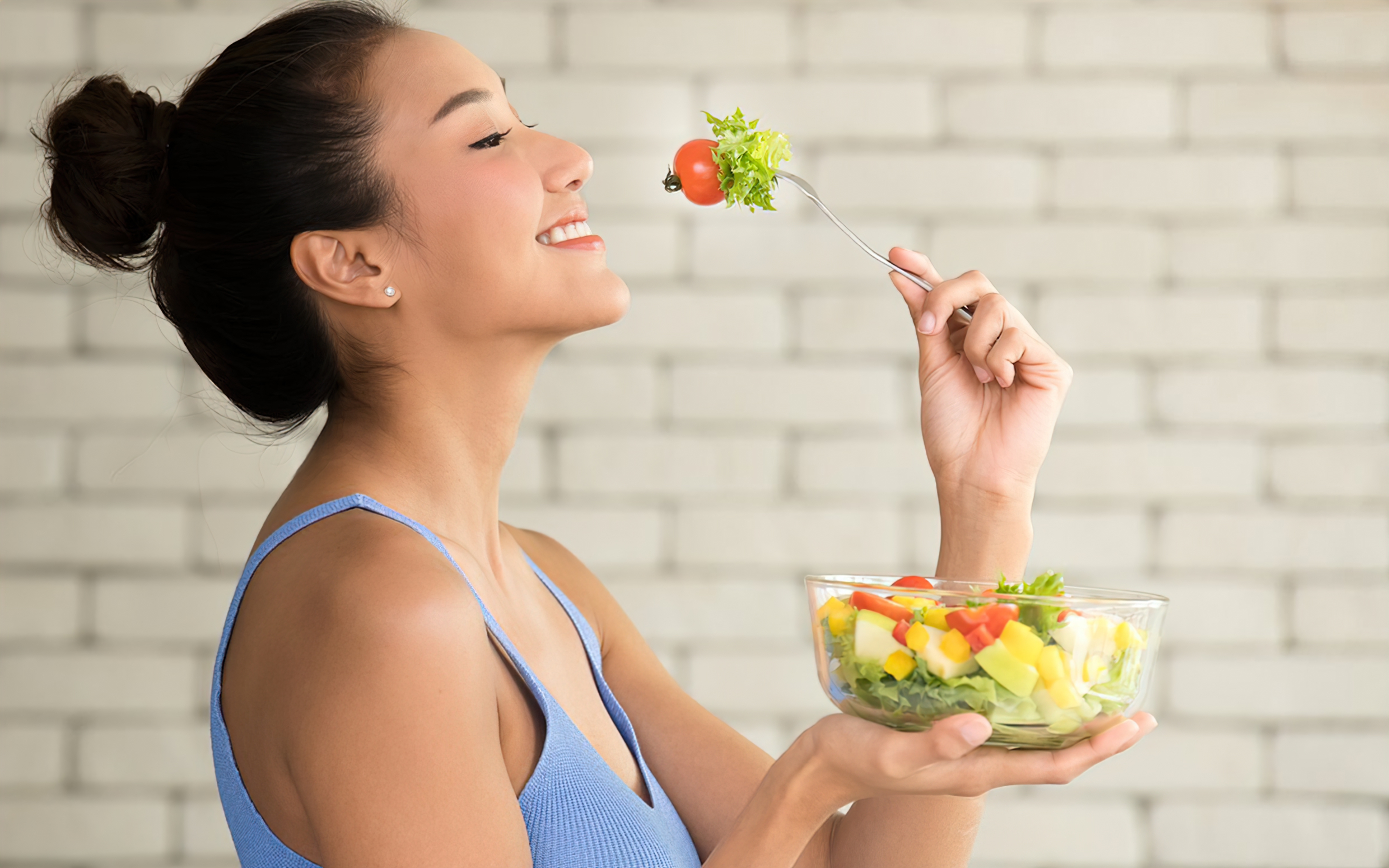

Another benefit of IF is weight loss. Losing weight can help improve insulin sensitivity, blood sugar control, and reduce the risk of heart disease. Intermittent fasting, when combined with a balanced diet and regular exercise, can be an effective weight loss strategy for diabetics. Additionally, IF has been shown to lower bad cholesterol (LDL) and triglyceride levels, further reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
-
Autophagy: A Cellular Cleanup Process for Better Health
Intermittent fasting can also promote autophagy, a cellular cleanup process that removes damaged cells and proteins from the body. This process can have potential benefits for diabetics by preventing the buildup of harmful cells and reducing inflammation. Studies have shown that autophagy can play a crucial role in improving insulin sensitivity and preventing complications associated with diabetes.
-
Choosing the Right Fasting Method: Find What Works for You

There are several IF methods to choose from, including the 16/8 method, the 5:2 method, and alternate-day fasting. The 16/8 method involves fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window each day, while the 5:2 method consists of eating normally for five days and consuming only 500-600 calories on two non-consecutive days. Alternate-day fasting involves fasting every other day, with some variations allowing for a small number of calories on fasting days. It’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any IF plan to ensure it’s suitable for your health and diabetes management.
-
Tips for Safely Incorporating IF into Your Diabetic Lifestyle

Before embarking on an intermittent fasting journey, it’s crucial to consider a few safety tips to ensure a smooth and healthy transition:
a. Consult with Your Healthcare Provider: Always discuss your plans with your doctor or diabetes care team before starting any new dietary regimen, including intermittent fasting. They can provide personalized guidance and monitor your progress.
b. Start Slowly: If you’re new to intermittent fasting, ease into the practice by gradually increasing your fasting duration. This approach allows your body to adjust and helps prevent extreme blood sugar fluctuations.
c. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly: Consistently check your blood sugar levels throughout the day, especially during fasting periods. This vigilance helps you maintain optimal glucose control and avoid hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
d. Prioritize Balanced Meals: When breaking your fast, focus on consuming nutrient-dense, balanced meals that include lean protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates. These foods will provide essential nutrients and help maintain steady blood sugar levels.
e. Stay Hydrated: Drinking water is vital during fasting periods, as it helps prevent dehydration and maintain proper bodily functions. Be sure to consume an adequate amount of water throughout the day, even when not eating.
f. Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body responds to intermittent fasting. If you experience dizziness, extreme fatigue, or persistent hunger, it may be a sign that IF isn’t suitable for you, or that you need to adjust your fasting method.
In summary, intermittent fasting can offer significant benefits for diabetics when done safely and under the guidance of healthcare professionals. By following the tips above and closely monitoring your blood sugar levels, you can unlock the potential of IF to improve your overall health and diabetes management.
